题目名称
- Regular Expression Matching(Leetcode #10)
- Longest Common Prefix(Leetcode #14)
- Valid Number(Leetcode #65)
- Integer to Roman(Leetcode #12)
- Anagrams(Leetcode #242)
- Simplify Path (Leetcode #242)
- Length of Last Word (Leetcode #58)
- Valid Parentheses (Leetcode #20)
- Largest Rectangle in Histogram(Leetcode #84)
- Evaluate Reverse Polish Notation (Leetcode #150)
Regular Expression Matching
题目描述
Given an input string (s) and a pattern (p), implement regular expression matching with support for ‘.’ and ‘*‘.
‘.’ Matches any single character.
‘*‘ Matches zero or more of the preceding element.
The matching should cover the entire input string (not partial).
Note:
s could be empty and contains only lowercase letters a-z.
p could be empty and contains only lowercase letters a-z, and characters like . or *.
Example 2:1
2
3
4
5Input:
s = "aa"
p = "a*"
Output: true
Explanation: '*' means zero or more of the precedeng element, 'a'. Therefore, by repeating 'a' once, it becomes "aa".
解题思路
本题采用递归完成。可以分为两个部分:第二个字符是’*‘与不是。若第二个字符不是,则直接比对当前第一个是否相等,若不相等返回false,相等则返回剩余部分是否相等。若第二个字符是’*‘,则问题可以分为两种情况:
- 若当前第一个字符不相等,忽略*(对应于匹配p.substr(2))。
- 若当前第一个相等,要么忽略*,要么删去当前的相等字符(s.substr(1))。
解题方案
1 | class Solution { |
扩展(Wildcard Matching Leetcode #44)
题目描述
Given an input string (s) and a pattern (p), implement wildcard pattern matching with support for ‘?’ and ‘*‘.
‘?’ Matches any single character.
‘*‘ Matches any sequence of characters (including the empty sequence).
The matching should cover the entire input string (not partial).
Note:
s could be empty and contains only lowercase letters a-z.
p could be empty and contains only lowercase letters a-z, and characters like ? or *.
Example 3:1
2
3
4
5Input:
s = "cb"
p = "?a"
Output: false
Explanation: '?' matches 'c', but the second letter is 'a', which does not match 'b'.
解题思路(递归)
递归解法的思路与上一题类似,若当前模式串字符为’*‘,则略过所有’*‘,若模式串略过’*‘后已到达尾部,必然匹配,否则递归式匹配s,p,若后者不匹配,++s,观察s是否为空(成功匹配)。
若当前模式串或主串为空,返回二者是否均为空。
若当前首字符相等,递归式匹配二者的下一个。
若当前不相等,不匹配。
本递归式解法时间复杂度为O(n!*m!),仅仅为了理解题意。
解题方案
1 | class Solution { |
解题思路(迭代)
主要是’*‘的匹配,p每遇到一个’*‘,就保留住当前’*‘坐标与s的坐标,然后s,若不成功则重新扫描。
解题方案(迭代)
1 | class Solution { |
Longest Common Prefix(Leetcode #14)
题目描述
Write a function to find the longest common prefix string amongst an array of strings.
If there is no common prefix, return an empty string “”.
Example 1:1
2Input: ["flower","flow","flight"]
Output: "fl"
解题思路
纵向比较,拿每个str与第一行相比配,不匹配当即返回。
解题方案
(由于STL的实现原因,下述代码不会导致数组越界)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12class Solution {
public:
string longestCommonPrefix(vector<string>& strs) {
if(strs.empty())
return "";
for(size_t i=0;i!=strs[0].size();++i){
for(size_t j=1;j!=strs.size();++j)
if(strs[j][i]!=strs[0][i]) return strs[0].substr(0,i);
}
return strs[0];
}
};
Valid Number (Leetcode #65)
解题思路
此题与我在解析JSON数字时十分相似,但JSON格式与此不太相同。此外,本题也可以使用有限自动机实现。
解题方案
1 | class Solution { |
Integer to Roman(Leetcode #12)
题目描述
Roman numerals are represented by seven different symbols: I, V, X, L, C, D and M.1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8Symbol Value
I 1
V 5
X 10
L 50
C 100
D 500
M 1000
For example, two is written as II in Roman numeral, just two one’s added together. Twelve is written as, XII, which is simply X + II. The number twenty seven is written as XXVII, which is XX + V + II.
Example:1
2
3Input: 58
Output: "LVIII"
Explanation: C = 100, L = 50, XXX = 30 and III = 3.
解题思路
本题存在两种解法,一种为O(1),非常奇怪的特解。一种为通用解。通用解的做法就是取出所有的单位(共13个),然后不断在string中加入。
解题方案
特解
1 | class Solution { |
通用解
1 | class Solution { |
扩展(Roman to Integer Leetcode#13)
题目描述
Example1:1
2Input: "IX"
Output: 9
Example2:1
2
3Input: "LVIII"
Output: 58
Explanation: C = 100, L = 50, XXX = 30 and III = 3.
解题思路
从后向前扫描,若第i位大于等于第i+1位,则加上第i位,否则减去。
解题方案
1 | class Solution { |
Anagrams(Leetcode #242)
题目描述
Given two strings s and t , write a function to determine if t is an anagram of s.
Example1:1
2Input: s = "anagram", t = "nagaram"
Output: true
Example2:1
2Input: s = "rat", t = "car"
Output: false
解题思路
相当容易的题目,以空间换时间即可。
解题方案
1 | class Solution { |
扩展(Group Anagrams Leetcode #49)
题目描述
Given an array of strings, group anagrams together.
Example:1
2
3
4
5
6
7Input: ["eat", "tea", "tan", "ate", "nat", "bat"],
Output:
[
["ate","eat","tea"],
["nat","tan"],
["bat"]
]
解题思路
从常规的角度来说,每一个放在一起的字符串排序之后必然相同,因此可以用一个hashtable<string,string>来存储结果,前一个string是排序结果,后一个是真实值。结着只要遍历vector即可。
本题另有一种巧妙解法,是人为地构建hash函数,每一组string对应一个独有的key。用一个map存储每个key对应的res数组的行号,若当前key已存储在map中,直接res[map[key]].push_back,否则在res中插入一个新的vector,并且更新map[key]=res.size()-1;
解题方案
排序
1 | class Solution { |
hash
1 | class Solution { |
Simplify Path (Leetcode #242)
题目描述
Given an absolute path for a file (Unix-style), simplify it.
For example,
path = “/home/“, => “/home”
path = “/a/./b/../../c/“, => “/c”
Corner Cases:
Did you consider the case where path = “/../“?
In this case, you should return “/“.
Another corner case is the path might contain multiple slashes ‘/‘ together, such as “/home//foo/“.In this case, you should ignore redundant slashes and return “/home/foo”.
解题思路
C++没有split,因此我们必须借助于getline(ss,temp,’/‘)。本题需要利用一个stack,当temp为””或”.”时直接无视,若temp为”..”且当前栈非空则pop,否则push temp。最后取出栈中元素,依次加上”/“。最后需要注意的是res若为空,返回的是”/“。
解题方案
1 | class Solution { |
Length of Last Word (Leetcode #58)
题目描述
Given a string s consists of upper/lower-case alphabets and empty space characters ‘ ‘, return the length of last word in the string.If the last word does not exist, return 0.
Note: A word is defined as a character sequence consists of non-space characters only.
Example:
Input: “Hello World”
Output: 5
解题思路
非常简单的题目,从后向前遍历,将第一个非” “字符设为起点,再将接下来的第一个” “设为终点即可。
解题方案
1 | class Solution { |
Valid Parentheses (Leetcode #20)
解题思路
栈的标准应用。
解题方案
1 | class Solution { |
扩展(Longest Valid Parentheses Leetcode #32)
题目描述
Given a string containing just the characters ‘(‘ and ‘)’, find the length of the longest valid (well-formed) parentheses substring.
Example:1
2
3Input: ")()())"
Output: 4
Explanation: The longest valid parentheses substring is "()()"
解题思路
用栈存储每一个’(‘的位置,并且设立last表征上一个不匹配点’)’的位置。若当前匹配,根据stk的情况更新maxlen。
解题方案
1 | class Solution { |
Largest Rectangle in Histogram(Leetcode #84)
题目描述
Given n non-negative integers representing the histogram’s bar height where the width of each bar is 1, find the area of largest rectangle in the histogram.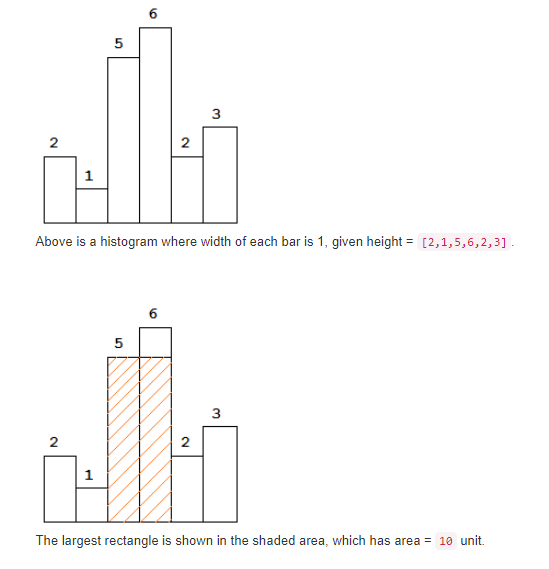
Example:1
2Input: [2,1,5,6,2,3]
Output: 10
解题思路
这道题十分类似于水库存水,解决方案是维护一个递增的栈,若当前元素小于栈顶,令其入栈,否则合并现有栈,直到栈顶元素小于当前元素。结尾是入栈元素0,再次完成合并。
解题方案
1 | class Solution { |
Evaluate Reverse Polish Notation (Leetcode #150)
题目描述
Evaluate the value of an arithmetic expression in Reverse Polish Notation.Valid operators are +, -, *, /. Each operand may be an integer or another expression.
Note:
Division between two integers should truncate toward zero.
The given RPN expression is always valid. That means the expression would always evaluate to a result and there won’t be any divide by zero operation.
Example:1
2
3Input: ["2", "1", "+", "3", "*"]
Output: 9
Explanation: ((2 + 1) * 3) = 9
解题思路
逆波兰表达式求值,栈的典型应用,没有难点,带有浮点数的中缀表达式求值才好玩。
解题方案
1 | class Solution { |
扩展(将中缀表达式变为后缀表达式)
解题思路
1 | map<char, int> isp = { { '(',1},{ '^',6},{ '*',5},{'/',5 },{'+',3},{'-',3},{')',7} }; |
- 遍历字符串
- 遇到数字直接rpn.push_back
- 遇到操作符
①如果是左括号 直接入栈
②如果是右括号,pop出栈内所有元素,直到遇到一个左括号,再pop掉左括号
③如果是操作运算符:
Ⅰ如果栈为空或者栈顶是左括号,入栈
Ⅱ如果当前字符的icp高于栈顶字符的isp,入栈
Ⅲ并不高于isp,弹出所有大于等于当前字符icp的操作符并且送入rpn,弹完之后把当前的push进去
④遍历结束,弹出栈内操作符,送入rpn